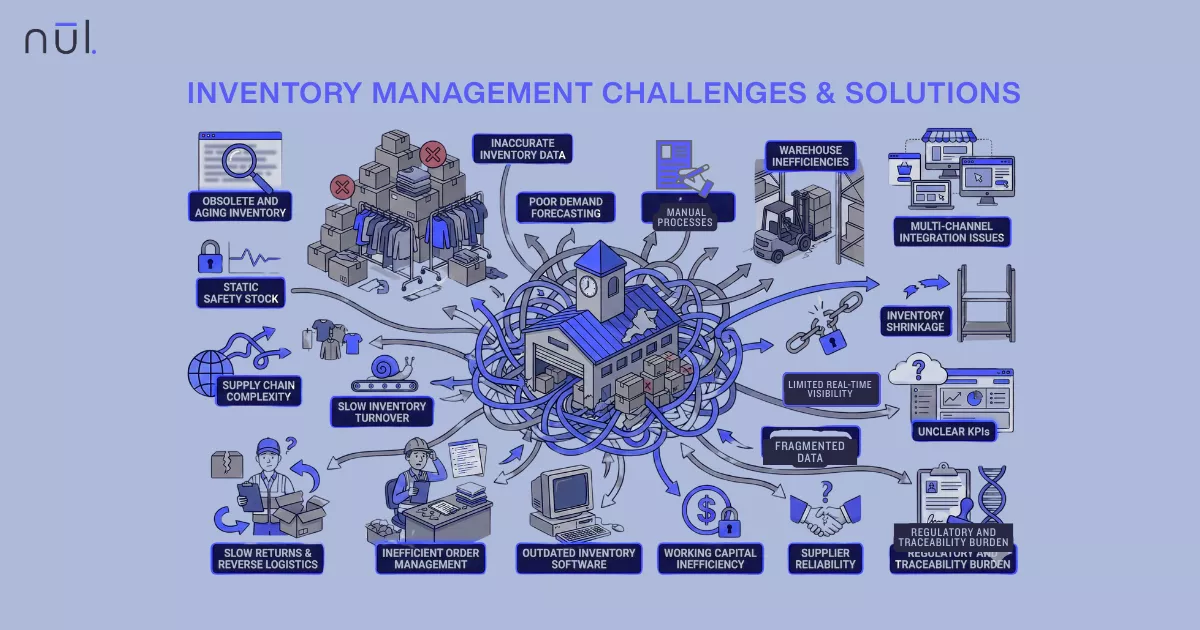
AI in Fashion Industry: 8 Use Cases, How‑To Guide, Pros & Cons
Aug 11, 2025
This blog helps you explore 8 common AI in fashion use cases, how to use AI in the fashion industry, and its positive and negative impacts on the industry.
AI is transforming every corner of the fashion industry, from predicting trends to reducing overproduction. If you’ve ever wondered how exactly fashion brands are using AI today (beyond the buzzwords), this guide breaks it all down.
Whether you’re running a label, working in merchandising, or just curious, here’s a practical, non-hypey look at how AI is actually used in fashion — with real examples, how-to guidance, benefits, and the risks. Let’s dive in.
AI in Fashion Market Size: How Big Is This Trend?
Before we get into the how, let’s look at the why. Why are fashion brands turning to AI, and how fast is this space growing?
The global AI in fashion market was valued at $1.26 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 40%, according to Research and Markets. At that pace, the market is expected to scale to tens of billions within the next decade, as more brands adopt AI across design, production, and retail.
In short, AI adoption in fashion is accelerating not just in R&D labs, but on shop floors, in merchandising teams, and throughout supply chains.
This growth is being driven by three major shifts:
The explosion of e-commerce and mobile shopping
Industry-wide pressure to reduce waste and overproduction
Greater accessibility of AI tools for non-technical teams
Now, let’s break down where AI is already making a real impact.

The global AI in fashion market. (Source: thebusinessresearchcompany.com)
8 AI in Fashion Use Cases
AI for Demand Forecasting
Fashion demand is highly unpredictable. Brands use AI to predict how much of each product will sell. So, they don’t overstock or run out too early.
How it works: AI models use machine learning to analyze historical sales data, seasonality, promotions, and external factors like weather or events. These models can forecast demand at the SKU level in weeks or months in advance.
Why it matters: Without accurate forecasting, fashion brands often overproduce (leading to waste) or underproduce (leading to missed sales). AI helps them strike the right balance.
Example: An activewear brand uses AI to predict how many units of each size to produce for a new sports bra launch. The model factors in past sales of similar products, search trends, and even gym membership data in their key markets.
>> Read more: Omnichannel Inventory Management: Challenges & How to Optimize?
AI for Trend Detection
Fashion trends move fast, often much faster than humans can track. With AI, brands can spot trend signals early, giving them an edge.
How it works: AI scans the internet, from TikTok to runway photos, to detect what styles, colors, or silhouettes are gaining popularity. These AI models are trained on image and text data to identify rising fashion elements. They can cluster similar images and track what’s trending by location, platform, or audience.
Why it matters: It’s hard for teams to manually keep up with trends across dozens of sources. AI gives an early signal, so brands can design or source faster. Catching a trend 2–3 months earlier can mean entering the market at just the right time, ahead of competitors.
Example: A streetwear label uses AI to spot an uptick in oversized outerwear in Southeast Asia two months before it hits Instagram Explore pages in the US.
AI for Visual Search
AI lets shoppers upload a photo and find similar-looking items in a brand’s catalog.
How it works: Image recognition models compare visual features (like color, texture, neckline, pattern) between a customer’s image and catalog SKUs, then identify the most visually similar items. Advanced models can also detect context clues like lighting, background, and whether the item is worn or laid flat.
Why it matters: Customers don’t always know how to describe what they want. Visual search removes the guesswork and makes discovery faster. This also creates a more intuitive, visual shopping experience that reduces frustration and shortens the path to purchase.
Example: A customer uploads a Pinterest outfit and instantly sees 5 similar jackets in the brand’s collection.
AI for Virtual Try-On
Online shoppers often hesitate due to fit uncertainty. AI solves that with immersive, real-time previews. Customers can see how clothes would look on them without trying them physically.
How it works: AI overlays garments on a user's body using computer vision and 3D fitting models. Some systems adjust fabric drape, movement, and lighting in real time.
Why it matters: Virtual try-on reduces returns and increases confidence in online shopping, especially for categories like swimwear or denim. The fewer returns a brand receives, the lower the logistics costs, carbon emissions, and customer service workload.
Example: A DTC swimwear brand lets shoppers see how a bikini fits on different body types in real time on their product pages.
AI for Pricing & Markdown Optimization
Pricing is one of the trickiest levers in fashion retail. If set too high, products collect dust. Go too low, and profits disappear. AI helps brands find the sweet spot automatically and continuously.
How it works: Machine learning models analyze sales velocity, inventory levels, competitor pricing, seasonality, and external factors like holidays or inflation to recommend optimal prices or markdown schedules. Some advanced tools allow A/B testing of pricing strategies by location, product category, or customer segment without manual effort.
Why it matters: It maximizes margin and minimizes deadstock, especially during sales periods or end-of-season clearances. This means more full-price sales, faster clearance cycles, and fewer end-of-season losses.
Example: A luxury accessories brand applies AI to evaluate sell-through trends by city. In markets with slower traction, the algorithm recommends earlier markdowns and tailored discount depths. In others, full pricing holds longer.
>> Read more:
AI for Sustainability & Waste Reduction
Fashion is responsible for nearly 10% of global carbon emissions. Much of this comes from overproduction, excess logistics, and poor forecasting. AI helps brands make smarter, leaner decisions that are good for both the planet and the bottom line.
How it works: AI improves demand planning, optimizes fabric usage, and suggests smaller, smarter batch production. Supply chain models identify lower-impact shipping routes and help reduce idle inventory sitting in warehouses. In circular fashion, AI sorts returned or secondhand garments by quality, style, and resale value.
Why it matters: Reducing fabric waste is firstly good for brand trust. It’s also a growing consumer demand and an operational necessity. AI empowers brands to produce what will actually sell, cut down excess, and lower return-related emissions.
Example: A slow fashion brand uses AI to simulate different production batch sizes and pick the one with the lowest unsold inventory risk.
>> Read more: 16 Best Inventory Cost Reduction Strategies for Fashion Brands
AI for Product Tagging & Catalog Management
Misspell a keyword or forget a style tag, and that product becomes invisible in search. AI fixes this by automating product descriptions, metadata tagging, and categorization.
How it works: Vision and language AI models scan product images and brief descriptions to generate rich metadata. They tag items with descriptors like “ruched sleeve,” “earth tone,” or “boho style”. These improve filtering, personalized search, and internal reporting.
Why it matters: Manual tagging is slow and inconsistent. AI makes catalog data more useful, especially when scaling SKUs.
Example: A marketplace uses AI to auto-tag 1,000 new products per day with consistent keywords that improve search results and SEO.
AI for Personalization & Styling
In a crowded online fashion space, personalization is no longer optional — it’s expected. AI helps brands create shopping experiences that feel tailored to each user, at scale.
How it works: AI recommendation systems analyze what shoppers viewed, liked, and bought, then suggest products that match their style, budget, and size. Some also learn from user feedback (e.g., dislikes, returns) to refine future suggestions. Deep learning models can even predict complementary items, creating complete outfits or personalized bundles.
Why it matters: Personalized shopping keeps users engaged longer and motivates them toward checkout. It also builds loyalty because customers are more likely to return when they feel understood.
Example: A multi-brand fashion platform shows different homepages to each user with personalized outfit bundles based on browsing history.

AI in Fashion Use Cases
How to Use AI in Your Fashion Brand? (Step-by-Step)
Identify the pain point: Are you overproducing? Do you have too many markdowns? Are customers dropping off?
Start small: Don’t try to do it all. Pick one AI use case (like demand forecasting or tagging) and run a pilot with a small category or campaign.
Prepare your data: AI is only as good as your data. That means you need to prepare consistent SKUs, inventory records, sales logs, and image libraries. If your data is messy, prioritize a cleanup phase first.
Work with experts: Depending on your team, you can build in-house tools, buy off-the-shelf solutions, or collaborate with experts like Nūl which offers ready-made AI systems for sustainable fashion retail.
Measure & iterate: Track outcomes like forecast accuracy, sell-through, and cost per unit. Use these insights to improve the model and expand to new use cases over time.
Pros of Using AI in Fashion
Reduces deadstock and waste through better planning and smarter inventory decisions.
Increases profit margins by optimizing pricing and reducing returns.
Improves customer experience with tailored recommendations and accurate search.
Speeds up internal workflows like tagging, catalog updates, and trend response.
Scales with ease without growing your merchandising or data teams.
Cons & Risks of AI in Fashion
Bias in training data can lead to lack of diversity in recommendations or design.
Requires good data hygiene, which some brands may not have.
Can’t replace human creativity, cultural insight, or emotional storytelling.
Integration hurdles with legacy ERP, CMS, or POS systems.
Overdependence on AI may reduce team skill development or creative confidence.
Conclusion
AI is changing how fashion brands work — from planning and pricing to personalization and sustainability. It’s not just about new tech trends in fashion, but about solving real fashion problems like overproduction, slow trend response, or poor customer experience.
The best way to start is small: choose one clear problem, get your data in shape, and test what works. With the right tools and mindset, AI can help fashion brands grow smarter, faster, and with less waste.

Article by
Nūl Content Team
An Experienced Research & Knowledge Team
The Nūl Content Team combines expertise in technology, fashion, and supply chain management to deliver clear, practical insights. Guided by Nūl’s mission to end overproduction, we create content that helps brands forecast demand more accurately, optimize inventory, and build sustainable operations. Every piece we publish is grounded in real-world experience, ensuring it’s both credible and actionable.
LinkedIn Profile
More From Blog
Co-Build With Us
We are so keen to get this right. If the problem statement resonates, please reach out and we’d love to co-build with you so fits right into your existing workflow.

Co-Build With Us
We are so keen to get this right. If the problem statement resonates, please reach out and we’d love to co-build with you so fits right into your existing workflow.


Co-Build With Us
We are so keen to get this right. If the problem statement resonates, please reach out and we’d love to co-build with you so fits right into your existing workflow.


More From Blog


AI in Fashion Industry: 8 Use Cases, How‑To Guide, Pros & Cons
Aug 11, 2025
This blog helps you explore 8 common AI in fashion use cases, how to use AI in the fashion industry, and its positive and negative impacts on the industry.
AI is transforming every corner of the fashion industry, from predicting trends to reducing overproduction. If you’ve ever wondered how exactly fashion brands are using AI today (beyond the buzzwords), this guide breaks it all down.
Whether you’re running a label, working in merchandising, or just curious, here’s a practical, non-hypey look at how AI is actually used in fashion — with real examples, how-to guidance, benefits, and the risks. Let’s dive in.
AI in Fashion Market Size: How Big Is This Trend?
Before we get into the how, let’s look at the why. Why are fashion brands turning to AI, and how fast is this space growing?
The global AI in fashion market was valued at $1.26 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 40%, according to Research and Markets. At that pace, the market is expected to scale to tens of billions within the next decade, as more brands adopt AI across design, production, and retail.
In short, AI adoption in fashion is accelerating not just in R&D labs, but on shop floors, in merchandising teams, and throughout supply chains.
This growth is being driven by three major shifts:
The explosion of e-commerce and mobile shopping
Industry-wide pressure to reduce waste and overproduction
Greater accessibility of AI tools for non-technical teams
Now, let’s break down where AI is already making a real impact.

The global AI in fashion market. (Source: thebusinessresearchcompany.com)
8 AI in Fashion Use Cases
AI for Demand Forecasting
Fashion demand is highly unpredictable. Brands use AI to predict how much of each product will sell. So, they don’t overstock or run out too early.
How it works: AI models use machine learning to analyze historical sales data, seasonality, promotions, and external factors like weather or events. These models can forecast demand at the SKU level in weeks or months in advance.
Why it matters: Without accurate forecasting, fashion brands often overproduce (leading to waste) or underproduce (leading to missed sales). AI helps them strike the right balance.
Example: An activewear brand uses AI to predict how many units of each size to produce for a new sports bra launch. The model factors in past sales of similar products, search trends, and even gym membership data in their key markets.
>> Read more: Omnichannel Inventory Management: Challenges & How to Optimize?
AI for Trend Detection
Fashion trends move fast, often much faster than humans can track. With AI, brands can spot trend signals early, giving them an edge.
How it works: AI scans the internet, from TikTok to runway photos, to detect what styles, colors, or silhouettes are gaining popularity. These AI models are trained on image and text data to identify rising fashion elements. They can cluster similar images and track what’s trending by location, platform, or audience.
Why it matters: It’s hard for teams to manually keep up with trends across dozens of sources. AI gives an early signal, so brands can design or source faster. Catching a trend 2–3 months earlier can mean entering the market at just the right time, ahead of competitors.
Example: A streetwear label uses AI to spot an uptick in oversized outerwear in Southeast Asia two months before it hits Instagram Explore pages in the US.
AI for Visual Search
AI lets shoppers upload a photo and find similar-looking items in a brand’s catalog.
How it works: Image recognition models compare visual features (like color, texture, neckline, pattern) between a customer’s image and catalog SKUs, then identify the most visually similar items. Advanced models can also detect context clues like lighting, background, and whether the item is worn or laid flat.
Why it matters: Customers don’t always know how to describe what they want. Visual search removes the guesswork and makes discovery faster. This also creates a more intuitive, visual shopping experience that reduces frustration and shortens the path to purchase.
Example: A customer uploads a Pinterest outfit and instantly sees 5 similar jackets in the brand’s collection.
AI for Virtual Try-On
Online shoppers often hesitate due to fit uncertainty. AI solves that with immersive, real-time previews. Customers can see how clothes would look on them without trying them physically.
How it works: AI overlays garments on a user's body using computer vision and 3D fitting models. Some systems adjust fabric drape, movement, and lighting in real time.
Why it matters: Virtual try-on reduces returns and increases confidence in online shopping, especially for categories like swimwear or denim. The fewer returns a brand receives, the lower the logistics costs, carbon emissions, and customer service workload.
Example: A DTC swimwear brand lets shoppers see how a bikini fits on different body types in real time on their product pages.
AI for Pricing & Markdown Optimization
Pricing is one of the trickiest levers in fashion retail. If set too high, products collect dust. Go too low, and profits disappear. AI helps brands find the sweet spot automatically and continuously.
How it works: Machine learning models analyze sales velocity, inventory levels, competitor pricing, seasonality, and external factors like holidays or inflation to recommend optimal prices or markdown schedules. Some advanced tools allow A/B testing of pricing strategies by location, product category, or customer segment without manual effort.
Why it matters: It maximizes margin and minimizes deadstock, especially during sales periods or end-of-season clearances. This means more full-price sales, faster clearance cycles, and fewer end-of-season losses.
Example: A luxury accessories brand applies AI to evaluate sell-through trends by city. In markets with slower traction, the algorithm recommends earlier markdowns and tailored discount depths. In others, full pricing holds longer.
>> Read more:
AI for Sustainability & Waste Reduction
Fashion is responsible for nearly 10% of global carbon emissions. Much of this comes from overproduction, excess logistics, and poor forecasting. AI helps brands make smarter, leaner decisions that are good for both the planet and the bottom line.
How it works: AI improves demand planning, optimizes fabric usage, and suggests smaller, smarter batch production. Supply chain models identify lower-impact shipping routes and help reduce idle inventory sitting in warehouses. In circular fashion, AI sorts returned or secondhand garments by quality, style, and resale value.
Why it matters: Reducing fabric waste is firstly good for brand trust. It’s also a growing consumer demand and an operational necessity. AI empowers brands to produce what will actually sell, cut down excess, and lower return-related emissions.
Example: A slow fashion brand uses AI to simulate different production batch sizes and pick the one with the lowest unsold inventory risk.
>> Read more: 16 Best Inventory Cost Reduction Strategies for Fashion Brands
AI for Product Tagging & Catalog Management
Misspell a keyword or forget a style tag, and that product becomes invisible in search. AI fixes this by automating product descriptions, metadata tagging, and categorization.
How it works: Vision and language AI models scan product images and brief descriptions to generate rich metadata. They tag items with descriptors like “ruched sleeve,” “earth tone,” or “boho style”. These improve filtering, personalized search, and internal reporting.
Why it matters: Manual tagging is slow and inconsistent. AI makes catalog data more useful, especially when scaling SKUs.
Example: A marketplace uses AI to auto-tag 1,000 new products per day with consistent keywords that improve search results and SEO.
AI for Personalization & Styling
In a crowded online fashion space, personalization is no longer optional — it’s expected. AI helps brands create shopping experiences that feel tailored to each user, at scale.
How it works: AI recommendation systems analyze what shoppers viewed, liked, and bought, then suggest products that match their style, budget, and size. Some also learn from user feedback (e.g., dislikes, returns) to refine future suggestions. Deep learning models can even predict complementary items, creating complete outfits or personalized bundles.
Why it matters: Personalized shopping keeps users engaged longer and motivates them toward checkout. It also builds loyalty because customers are more likely to return when they feel understood.
Example: A multi-brand fashion platform shows different homepages to each user with personalized outfit bundles based on browsing history.

AI in Fashion Use Cases
How to Use AI in Your Fashion Brand? (Step-by-Step)
Identify the pain point: Are you overproducing? Do you have too many markdowns? Are customers dropping off?
Start small: Don’t try to do it all. Pick one AI use case (like demand forecasting or tagging) and run a pilot with a small category or campaign.
Prepare your data: AI is only as good as your data. That means you need to prepare consistent SKUs, inventory records, sales logs, and image libraries. If your data is messy, prioritize a cleanup phase first.
Work with experts: Depending on your team, you can build in-house tools, buy off-the-shelf solutions, or collaborate with experts like Nūl which offers ready-made AI systems for sustainable fashion retail.
Measure & iterate: Track outcomes like forecast accuracy, sell-through, and cost per unit. Use these insights to improve the model and expand to new use cases over time.
Pros of Using AI in Fashion
Reduces deadstock and waste through better planning and smarter inventory decisions.
Increases profit margins by optimizing pricing and reducing returns.
Improves customer experience with tailored recommendations and accurate search.
Speeds up internal workflows like tagging, catalog updates, and trend response.
Scales with ease without growing your merchandising or data teams.
Cons & Risks of AI in Fashion
Bias in training data can lead to lack of diversity in recommendations or design.
Requires good data hygiene, which some brands may not have.
Can’t replace human creativity, cultural insight, or emotional storytelling.
Integration hurdles with legacy ERP, CMS, or POS systems.
Overdependence on AI may reduce team skill development or creative confidence.
Conclusion
AI is changing how fashion brands work — from planning and pricing to personalization and sustainability. It’s not just about new tech trends in fashion, but about solving real fashion problems like overproduction, slow trend response, or poor customer experience.
The best way to start is small: choose one clear problem, get your data in shape, and test what works. With the right tools and mindset, AI can help fashion brands grow smarter, faster, and with less waste.


Article by
Nūl Content Team
An Experienced Research & Knowledge Team
An Experienced Research & Knowledge Team
The Nūl Content Team combines expertise in technology, fashion, and supply chain management to deliver clear, practical insights. Guided by Nūl’s mission to end overproduction, we create content that helps brands forecast demand more accurately, optimize inventory, and build sustainable operations. Every piece we publish is grounded in real-world experience, ensuring it’s both credible and actionable.
LinkedIn Profile