16 Best Inventory Cost Reduction Strategies for Fashion Brands
Nov 19, 2025
Audit current costs, Improve demand forecasting, Automate inventory replenishment, Remove obsolete/slow-moving stock,... are the inventory cost reduction strategies.
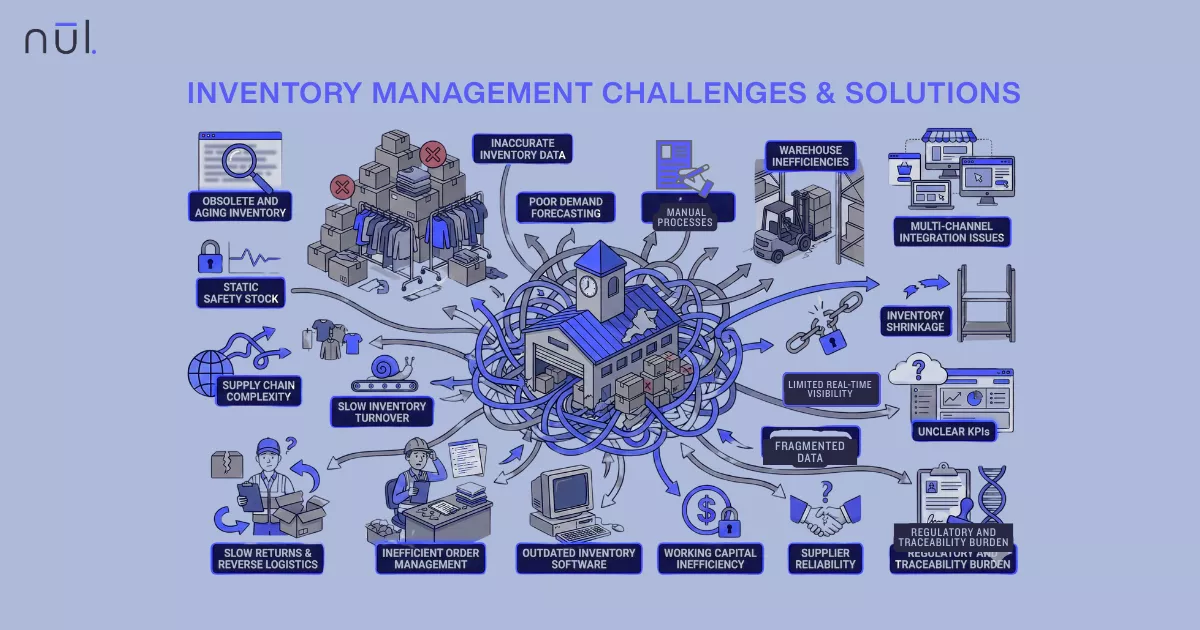
Inventory is the largest cost driver in fashion — spanning raw materials, production, warehousing, logistics, markdowns, and returns. Every unit sitting too long in storage quietly increases total costs, which include:
Ordering costs (procurement and setup),
Carrying costs (capital, insurance, and depreciation),
Holding costs (storage and labor),
Stock-out costs (lost sales and customer dissatisfaction),
Obsolescence costs (unsellable or outdated items),
Shrinkage costs (theft, damage, or record errors),
More.
For manufacturers, retailers, and eCommerce brands, smart inventory management is one of the fastest ways to protect margins and improve cash flow. This guide covers 16 practical, data-driven strategies to reduce inventory holding costs, improve forecasting accuracy, and move toward a leaner, zero-waste fashion supply chain.

Inventory costs can increase total costs.
Audit Your Current Inventory Costs
Intent: Understand where your money is tied up before making reductions.
Action:
Map major cost drivers across all stages like sourcing, production, warehousing, logistics, retail distribution, and product returns. Also include hidden costs like damaged goods, repackaging, markdowns, and storage inefficiency.
Calculate key metrics like Carrying Cost %, Days Sales of Inventory (DSI), Turnover Ratio, and Write-Off %. These reveal where money leaks occur.
Use ERP or cloud-based tools for SKU-level cost visibility. Integrate data from PLM, POS, and warehouse systems to unify reporting across all channels.
Create automated reports showing cost concentration by product category, supplier, season, or collection. Highlight slow-moving items, high storage expenses, or high return rates.
Compare actual carrying costs against industry standards to identify areas needing leaner inventory policies or supplier renegotiation.
Result: A clear dashboard showing which products, suppliers, or collections consume the most working capital. Your team have a clear starting point for targeted cost reduction.
Improve Demand Forecast Accuracy
Intent: Prevent overstock and stockouts through smarter, data-driven forecasting.
Action:
Analyze historical sales by collection, color, size, and region, promotions, and seasonal shifts to identify recurring demand trends. Factor in fashion cycles, weather changes, holidays, social media trends, and influencer-driven spikes that can shift buying behavior.
Apply statistical models like moving averages, regression or AI/ML to forecast demand at SKU or store level, incorporating real-time signals such as Google Trends, social mentions, or sell-through data. Consider using AI-driven forecasting software to automate pattern detection and predict future sell-through rates.
Integrate data from eCommerce, POS, and wholesale channels form a unified demand picture, then sync these insights directly into your ERP or OMS for immediate production and replenishment planning.
Track forecast error metrics such as MAPE or WAPE monthly, then adjust models based on promotions, returns, or sell-out speed.
Result: More accurate demand forecasting, balanced stock levels, fewer unsold items, and stronger cash flow across every sales channel.
Automate Inventory Replenishment
Intent: Replenish inventory at the right time automatically to maintain availability and reduce manual effort.
Use the formula
(Average Daily Usage × Lead Time) + Safety Stockto determine when to reorder each SKU. In fashion, this ensures timely replenishment of fast-selling sizes or colors before they sell out.Apply dynamic reorder logic that adapts to demand fluctuations during sales, product launches, or new collections.
Use AI-driven inventory management software to automate reorder logic adjustment based on recent demand trends, lead-time changes, and seasonality.
Use automation tools that can trigger purchase orders when stock hits reorder thresholds to prevent manual delays.
Match your reorder points to your suppliers’ real delivery times. If suppliers take longer or deliver earlier than expected, adjust your reorder levels to keep stock balanced.
Result: Smarter, faster replenishment cycles with fewer stockouts, less overstock, lower carrying costs, and fewer emergency purchases.
>> Explore further: 10 Best Inventory Replenishment Software Solutions
Eliminate Obsolete and Slow-Moving Stock
Intent: Identify and clear aging products that no longer sell to recover cash and optimize inventory health.
Action:
Classify SKUs by using ABC analysis to rank products by value as A (high-value, high-impact), B (moderate value), and C (low value). Combine it with FSN analysis to categorize items as Fast, Slow, or Non-moving based on inventory velocity.
Apply tighter monitoring, safety stock control, and replenishment planning for A and Fast-moving items that drive most of your revenue.
Regularly clear C-class or Non-moving products, SKUs with little or no sales activity (typically 90–180 days), often called aged inventory, through markdown strategies, bundles, or liquidation to free up capital and inventory storage.
Investigate why items became slow-moving like overproduction, trend mismatch, poor size ratios, or inaccurate forecasts, and use insights to adjust future buying and planning decisions.
Automate classification and reporting through ERP or analytics dashboards for real-time visibility into slow-moving inventory.
Result: Leaner assortments, faster cash turnover, and reduced losses from outdated or unsellable SKUs.
Adopt Lean Inventory Practices
Intent: Eliminate waste across fashion inventory operations.
Action:
Use RFID or barcode scanning to record items instantly and store them directly in assigned zones to avoid double handling.
Implement batch picking or Pick-to-Light fulfillment to reduce walking distance and speed up order processing.
Shift from large seasonal production runs to smaller, frequent micro-replenishments triggered by real-time sales data.
Result: Lower labor costs, reduced storage waste, and faster stock movement.
Apply Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
Intent: Align material sourcing and production closely with actual demand.
Action:
Coordinate production with confirmed purchase orders. This means manufacturing only begins after receiving confirmed retail or wholesale purchase orders to avoid overproduction.
Use ERP or supplier portals to automate purchase orders, track deliveries, and sync production schedules in real time.
Maintain only minimal safety stock for volatility without carrying excess inventory.
Work with nearshore or fast-response partners capable of small-batch, quick-turnaround production.
Result: Reduced storage, insurance, and obsolescence costs while reducing markdown risk and increasing cash flexibility.
Establish Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
Intent: Share stock responsibility with suppliers.
Action:
Allow vendors to monitor your stock levels and replenish items automatically based on real-time sales and usage data.
Integrate ERP or EDI systems for real-time synchronization, sharing demand forecasts and product movement reports for suppliers to plan production more efficiently.
Result: Lower administrative burden, better supplier alignment, and fewer stockouts.
Shorten Supplier Lead Times
Intent: Increase responsiveness and reduce dependence on large safety stock.
Action:
Negotiate faster production and shipping timelines with key suppliers.
Diversify sourcing or move part of production closer to demand regions.
Track supplier reliability with performance scorecards.
Result: Reduced buffer inventory, faster replenishment, and stronger agility.
Reduce Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs)
Intent: Prevent overbuying and excess stock.
Action:
Negotiate smaller batch sizes using real-time sales and demand forecasts. When suppliers see consistent, data-backed sell-through, they’re more open to smaller, flexible order quantities
Group SKUs with similar materials, trims, or colors to meet supplier thresholds instead of large, single-style orders. This approach reduces leftover fabric and components across collections.
Work with nearshore or digitally enabled factories that specialize in smaller production runs and rapid turnarounds. These partners often use automated cutting, digital patterning, or on-demand printing to lower setup costs and support leaner production.
Use supplier portals or sourcing platforms to connect with vendors that accommodate variable batch sizes and allow quicker reorders as sales data updates.
Result: Leaner inbound stock and healthier cash flow.
Optimize Warehouse Layout and Handling
Intent: Improve speed and reduce operational costs.
Action:
Store high-frequency or high-margin SKUs near dispatch areas for faster access. Group items by size, color, or style to minimize travel distance and simplify picking for fashion assortments.
Use slotting optimization to minimize travel time. WMS analytics can assign locations based on item turnover rates. Automatically re-slot products when demand patterns change between seasons or collections.
Introduce ergonomic tools for faster picking like adjustable packing stations, lightweight carts, and optimized shelving heights.
Analyze metrics such as average picking time, travel distance per order, and labor utilization to identify new efficiency opportunities.
Result: Faster fulfillment, fewer handling errors, and lower labor costs.

Optimize Warehouse Layout and Handling
Implement Cycle Counting and Real-Time Tracking
Intent: Maintain accuracy without costly full audits.
Action:
Replace annual stocktakes with continuous cycle counts. scheduled by product category or location. Prioritize high-value or fast-moving SKUs for more frequent checks while reviewing slower items less often.
Use IoT sensors or RFID tags for real-time visibility of stock movement when items are received, picked, or shipped. This eliminates manual entry errors and keeps your system current at all times.
Review variance reports regularly to identify shrinkage, misplacement, or scanning errors before they become costly write-offs.
Result: Improved stock accuracy and fewer write-offs.
Strengthen Supplier Collaboration
Intent: Build resilient, transparent supply chains that improve responsiveness and reduce inventory risk.
Share forecasts, inventory data , and replenishment schedules via supplier portals or shared dashboards. This helps suppliers anticipate demand and plan capacity more accurately.
Hold joint planning sessions via digital collaboration tools to align production with demand.
Reward suppliers for meeting lead-time targets, maintaining quality consistency, and offering flexibility in order quantities. Structured scorecards or tiered incentives encourage accountability.
Prioritize suppliers who apply transparency, data sharing, and sustainability practices to build a more resilient supply chain.
Result: Fewer shortages, smoother operations, and stronger partnerships.
Review and Adjust Safety Stock Policies
Intent: Prevent overstocking while ensuring service levels.
Action:
Recalculate safety stock based on demand variability, lead time, and service level goals rather than fixed estimates. For example, base buffer levels on standard deviation of demand and average supplier delay.
Differentiate targets by product criticality. Keep tighter buffers for essentials and minimal ones for trend-driven or short-lifecycle products.
Update calculations automatically as new sales, production, or supplier data becomes available. Use integrated ERP or forecasting tools to adjust buffer levels dynamically.
Result: 10–20% reduction in carrying costs with consistent fulfillment.
Use Inventory Optimization Software
Intent: Improve decision-making with analytics and automation.
Action:
Deploy cloud tools integrating ERP, POS, and WMS data. You will have a unified view of stock levels, sales velocity, and supplier performance across all channels.
Use AI-driven modules for inventory management, forecasting, and order optimization. They can also recommend optimal stock levels and reorder quantities by SKU, style, or store.
Let the software generate purchase or production plans automatically based on live sales and lead-time data, reducing manual errors and reaction time.
Use dashboards and alerts to track inventory turnover, dead stock, and upcoming shortages instantly, helping teams make quick, data-backed decisions.
Review software insights regularly to refine parameters like reorder frequency, supplier reliability, and safety stock targets for better ROI.
Result: Smarter inventory planning with real-time visibility.

Use Inventory Optimization Software
Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Intent: Measure progress and guide continuous improvement.
Action:
Monitor metrics like DSI, turnover ratio, carrying cost %, and order accuracy to assess how efficiently inventory is managed.
Break KPIs down by product line, supplier, or sales channel to pinpoint specific areas causing cost overruns or slow movement.
Visualize data in automated dashboards.
Compare current metrics against historical data or industry standards to identify gaps and track improvement trends over time.
Use alerts or exception reports to flag issues early
Result: Real-time performance tracking and accountability.
Build a Continuous Improvement Culture
Intent: Make cost reduction a long-term mindset.
Action:
Encourage collaboration between finance, operations, procurement, , merchandising, and logistics in regular reviews to align cost objectives with business goals.
Conduct quarterly reviews and implement Kaizen or PDCA methods to evaluate processes, test solutions, and measure outcomes systematically.
Celebrate teams that achieve measurable cost savings or process innovations, and replicate their methods across other departments.
Result: Sustained efficiency and compounding savings across the business.
Conclusion
Reducing inventory costs isn’t about cutting stock blindly — it’s about making smarter, faster, data-backed decisions. Start by auditing your current costs, implement 3–4 quick-win strategies, and track KPIs monthly to measure ROI. As accuracy improves, you’ll reduce holding costs, boost margins, and move closer to a truly zero-waste inventory model.
Smart inventory management is not just a cost strategy — it’s a growth strategy.

Article by
Nūl Content Team
An Experienced Research & Knowledge Team
The Nūl Content Team combines expertise in technology, fashion, and supply chain management to deliver clear, practical insights. Guided by Nūl’s mission to end overproduction, we create content that helps brands forecast demand more accurately, optimize inventory, and build sustainable operations. Every piece we publish is grounded in real-world experience, ensuring it’s both credible and actionable.
LinkedIn Profile
More From Blog
Co-Build With Us
We are so keen to get this right. If the problem statement resonates, please reach out and we’d love to co-build with you so fits right into your existing workflow.

Co-Build With Us
We are so keen to get this right. If the problem statement resonates, please reach out and we’d love to co-build with you so fits right into your existing workflow.


Co-Build With Us
We are so keen to get this right. If the problem statement resonates, please reach out and we’d love to co-build with you so fits right into your existing workflow.


More From Blog


16 Best Inventory Cost Reduction Strategies for Fashion Brands
Nov 19, 2025
Audit current costs, Improve demand forecasting, Automate inventory replenishment, Remove obsolete/slow-moving stock,... are the inventory cost reduction strategies.
Inventory is the largest cost driver in fashion — spanning raw materials, production, warehousing, logistics, markdowns, and returns. Every unit sitting too long in storage quietly increases total costs, which include:
Ordering costs (procurement and setup),
Carrying costs (capital, insurance, and depreciation),
Holding costs (storage and labor),
Stock-out costs (lost sales and customer dissatisfaction),
Obsolescence costs (unsellable or outdated items),
Shrinkage costs (theft, damage, or record errors),
More.
For manufacturers, retailers, and eCommerce brands, smart inventory management is one of the fastest ways to protect margins and improve cash flow. This guide covers 16 practical, data-driven strategies to reduce inventory holding costs, improve forecasting accuracy, and move toward a leaner, zero-waste fashion supply chain.

Inventory costs can increase total costs.
Audit Your Current Inventory Costs
Intent: Understand where your money is tied up before making reductions.
Action:
Map major cost drivers across all stages like sourcing, production, warehousing, logistics, retail distribution, and product returns. Also include hidden costs like damaged goods, repackaging, markdowns, and storage inefficiency.
Calculate key metrics like Carrying Cost %, Days Sales of Inventory (DSI), Turnover Ratio, and Write-Off %. These reveal where money leaks occur.
Use ERP or cloud-based tools for SKU-level cost visibility. Integrate data from PLM, POS, and warehouse systems to unify reporting across all channels.
Create automated reports showing cost concentration by product category, supplier, season, or collection. Highlight slow-moving items, high storage expenses, or high return rates.
Compare actual carrying costs against industry standards to identify areas needing leaner inventory policies or supplier renegotiation.
Result: A clear dashboard showing which products, suppliers, or collections consume the most working capital. Your team have a clear starting point for targeted cost reduction.
Improve Demand Forecast Accuracy
Intent: Prevent overstock and stockouts through smarter, data-driven forecasting.
Action:
Analyze historical sales by collection, color, size, and region, promotions, and seasonal shifts to identify recurring demand trends. Factor in fashion cycles, weather changes, holidays, social media trends, and influencer-driven spikes that can shift buying behavior.
Apply statistical models like moving averages, regression or AI/ML to forecast demand at SKU or store level, incorporating real-time signals such as Google Trends, social mentions, or sell-through data. Consider using AI-driven forecasting software to automate pattern detection and predict future sell-through rates.
Integrate data from eCommerce, POS, and wholesale channels form a unified demand picture, then sync these insights directly into your ERP or OMS for immediate production and replenishment planning.
Track forecast error metrics such as MAPE or WAPE monthly, then adjust models based on promotions, returns, or sell-out speed.
Result: More accurate demand forecasting, balanced stock levels, fewer unsold items, and stronger cash flow across every sales channel.
Automate Inventory Replenishment
Intent: Replenish inventory at the right time automatically to maintain availability and reduce manual effort.
Use the formula
(Average Daily Usage × Lead Time) + Safety Stockto determine when to reorder each SKU. In fashion, this ensures timely replenishment of fast-selling sizes or colors before they sell out.Apply dynamic reorder logic that adapts to demand fluctuations during sales, product launches, or new collections.
Use AI-driven inventory management software to automate reorder logic adjustment based on recent demand trends, lead-time changes, and seasonality.
Use automation tools that can trigger purchase orders when stock hits reorder thresholds to prevent manual delays.
Match your reorder points to your suppliers’ real delivery times. If suppliers take longer or deliver earlier than expected, adjust your reorder levels to keep stock balanced.
Result: Smarter, faster replenishment cycles with fewer stockouts, less overstock, lower carrying costs, and fewer emergency purchases.
>> Explore further: 10 Best Inventory Replenishment Software Solutions
Eliminate Obsolete and Slow-Moving Stock
Intent: Identify and clear aging products that no longer sell to recover cash and optimize inventory health.
Action:
Classify SKUs by using ABC analysis to rank products by value as A (high-value, high-impact), B (moderate value), and C (low value). Combine it with FSN analysis to categorize items as Fast, Slow, or Non-moving based on inventory velocity.
Apply tighter monitoring, safety stock control, and replenishment planning for A and Fast-moving items that drive most of your revenue.
Regularly clear C-class or Non-moving products, SKUs with little or no sales activity (typically 90–180 days), often called aged inventory, through markdown strategies, bundles, or liquidation to free up capital and inventory storage.
Investigate why items became slow-moving like overproduction, trend mismatch, poor size ratios, or inaccurate forecasts, and use insights to adjust future buying and planning decisions.
Automate classification and reporting through ERP or analytics dashboards for real-time visibility into slow-moving inventory.
Result: Leaner assortments, faster cash turnover, and reduced losses from outdated or unsellable SKUs.
Adopt Lean Inventory Practices
Intent: Eliminate waste across fashion inventory operations.
Action:
Use RFID or barcode scanning to record items instantly and store them directly in assigned zones to avoid double handling.
Implement batch picking or Pick-to-Light fulfillment to reduce walking distance and speed up order processing.
Shift from large seasonal production runs to smaller, frequent micro-replenishments triggered by real-time sales data.
Result: Lower labor costs, reduced storage waste, and faster stock movement.
Apply Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
Intent: Align material sourcing and production closely with actual demand.
Action:
Coordinate production with confirmed purchase orders. This means manufacturing only begins after receiving confirmed retail or wholesale purchase orders to avoid overproduction.
Use ERP or supplier portals to automate purchase orders, track deliveries, and sync production schedules in real time.
Maintain only minimal safety stock for volatility without carrying excess inventory.
Work with nearshore or fast-response partners capable of small-batch, quick-turnaround production.
Result: Reduced storage, insurance, and obsolescence costs while reducing markdown risk and increasing cash flexibility.
Establish Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
Intent: Share stock responsibility with suppliers.
Action:
Allow vendors to monitor your stock levels and replenish items automatically based on real-time sales and usage data.
Integrate ERP or EDI systems for real-time synchronization, sharing demand forecasts and product movement reports for suppliers to plan production more efficiently.
Result: Lower administrative burden, better supplier alignment, and fewer stockouts.
Shorten Supplier Lead Times
Intent: Increase responsiveness and reduce dependence on large safety stock.
Action:
Negotiate faster production and shipping timelines with key suppliers.
Diversify sourcing or move part of production closer to demand regions.
Track supplier reliability with performance scorecards.
Result: Reduced buffer inventory, faster replenishment, and stronger agility.
Reduce Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs)
Intent: Prevent overbuying and excess stock.
Action:
Negotiate smaller batch sizes using real-time sales and demand forecasts. When suppliers see consistent, data-backed sell-through, they’re more open to smaller, flexible order quantities
Group SKUs with similar materials, trims, or colors to meet supplier thresholds instead of large, single-style orders. This approach reduces leftover fabric and components across collections.
Work with nearshore or digitally enabled factories that specialize in smaller production runs and rapid turnarounds. These partners often use automated cutting, digital patterning, or on-demand printing to lower setup costs and support leaner production.
Use supplier portals or sourcing platforms to connect with vendors that accommodate variable batch sizes and allow quicker reorders as sales data updates.
Result: Leaner inbound stock and healthier cash flow.
Optimize Warehouse Layout and Handling
Intent: Improve speed and reduce operational costs.
Action:
Store high-frequency or high-margin SKUs near dispatch areas for faster access. Group items by size, color, or style to minimize travel distance and simplify picking for fashion assortments.
Use slotting optimization to minimize travel time. WMS analytics can assign locations based on item turnover rates. Automatically re-slot products when demand patterns change between seasons or collections.
Introduce ergonomic tools for faster picking like adjustable packing stations, lightweight carts, and optimized shelving heights.
Analyze metrics such as average picking time, travel distance per order, and labor utilization to identify new efficiency opportunities.
Result: Faster fulfillment, fewer handling errors, and lower labor costs.

Optimize Warehouse Layout and Handling
Implement Cycle Counting and Real-Time Tracking
Intent: Maintain accuracy without costly full audits.
Action:
Replace annual stocktakes with continuous cycle counts. scheduled by product category or location. Prioritize high-value or fast-moving SKUs for more frequent checks while reviewing slower items less often.
Use IoT sensors or RFID tags for real-time visibility of stock movement when items are received, picked, or shipped. This eliminates manual entry errors and keeps your system current at all times.
Review variance reports regularly to identify shrinkage, misplacement, or scanning errors before they become costly write-offs.
Result: Improved stock accuracy and fewer write-offs.
Strengthen Supplier Collaboration
Intent: Build resilient, transparent supply chains that improve responsiveness and reduce inventory risk.
Share forecasts, inventory data , and replenishment schedules via supplier portals or shared dashboards. This helps suppliers anticipate demand and plan capacity more accurately.
Hold joint planning sessions via digital collaboration tools to align production with demand.
Reward suppliers for meeting lead-time targets, maintaining quality consistency, and offering flexibility in order quantities. Structured scorecards or tiered incentives encourage accountability.
Prioritize suppliers who apply transparency, data sharing, and sustainability practices to build a more resilient supply chain.
Result: Fewer shortages, smoother operations, and stronger partnerships.
Review and Adjust Safety Stock Policies
Intent: Prevent overstocking while ensuring service levels.
Action:
Recalculate safety stock based on demand variability, lead time, and service level goals rather than fixed estimates. For example, base buffer levels on standard deviation of demand and average supplier delay.
Differentiate targets by product criticality. Keep tighter buffers for essentials and minimal ones for trend-driven or short-lifecycle products.
Update calculations automatically as new sales, production, or supplier data becomes available. Use integrated ERP or forecasting tools to adjust buffer levels dynamically.
Result: 10–20% reduction in carrying costs with consistent fulfillment.
Use Inventory Optimization Software
Intent: Improve decision-making with analytics and automation.
Action:
Deploy cloud tools integrating ERP, POS, and WMS data. You will have a unified view of stock levels, sales velocity, and supplier performance across all channels.
Use AI-driven modules for inventory management, forecasting, and order optimization. They can also recommend optimal stock levels and reorder quantities by SKU, style, or store.
Let the software generate purchase or production plans automatically based on live sales and lead-time data, reducing manual errors and reaction time.
Use dashboards and alerts to track inventory turnover, dead stock, and upcoming shortages instantly, helping teams make quick, data-backed decisions.
Review software insights regularly to refine parameters like reorder frequency, supplier reliability, and safety stock targets for better ROI.
Result: Smarter inventory planning with real-time visibility.

Use Inventory Optimization Software
Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Intent: Measure progress and guide continuous improvement.
Action:
Monitor metrics like DSI, turnover ratio, carrying cost %, and order accuracy to assess how efficiently inventory is managed.
Break KPIs down by product line, supplier, or sales channel to pinpoint specific areas causing cost overruns or slow movement.
Visualize data in automated dashboards.
Compare current metrics against historical data or industry standards to identify gaps and track improvement trends over time.
Use alerts or exception reports to flag issues early
Result: Real-time performance tracking and accountability.
Build a Continuous Improvement Culture
Intent: Make cost reduction a long-term mindset.
Action:
Encourage collaboration between finance, operations, procurement, , merchandising, and logistics in regular reviews to align cost objectives with business goals.
Conduct quarterly reviews and implement Kaizen or PDCA methods to evaluate processes, test solutions, and measure outcomes systematically.
Celebrate teams that achieve measurable cost savings or process innovations, and replicate their methods across other departments.
Result: Sustained efficiency and compounding savings across the business.
Conclusion
Reducing inventory costs isn’t about cutting stock blindly — it’s about making smarter, faster, data-backed decisions. Start by auditing your current costs, implement 3–4 quick-win strategies, and track KPIs monthly to measure ROI. As accuracy improves, you’ll reduce holding costs, boost margins, and move closer to a truly zero-waste inventory model.
Smart inventory management is not just a cost strategy — it’s a growth strategy.


Article by
Nūl Content Team
An Experienced Research & Knowledge Team
An Experienced Research & Knowledge Team
The Nūl Content Team combines expertise in technology, fashion, and supply chain management to deliver clear, practical insights. Guided by Nūl’s mission to end overproduction, we create content that helps brands forecast demand more accurately, optimize inventory, and build sustainable operations. Every piece we publish is grounded in real-world experience, ensuring it’s both credible and actionable.
LinkedIn Profile