Inventory Replenishment: Process, Methods, Best Practices
Sep 30, 2025
Inventory replenishment is the process of restocking products to maintain the right balance between supply and demand, and prevent overstock of slow-moving goods.
Inventory is the lifeblood of any business—whether you’re a fashion retailer, an eCommerce brand, a wholesaler, or a manufacturer. Too little stock, and you lose sales. Too much, and you tie up cash while risking waste. That’s where inventory replenishment comes in.
This article explains what inventory replenishment is, how the process works, the methods businesses use, common challenges, and best practices for getting it right.
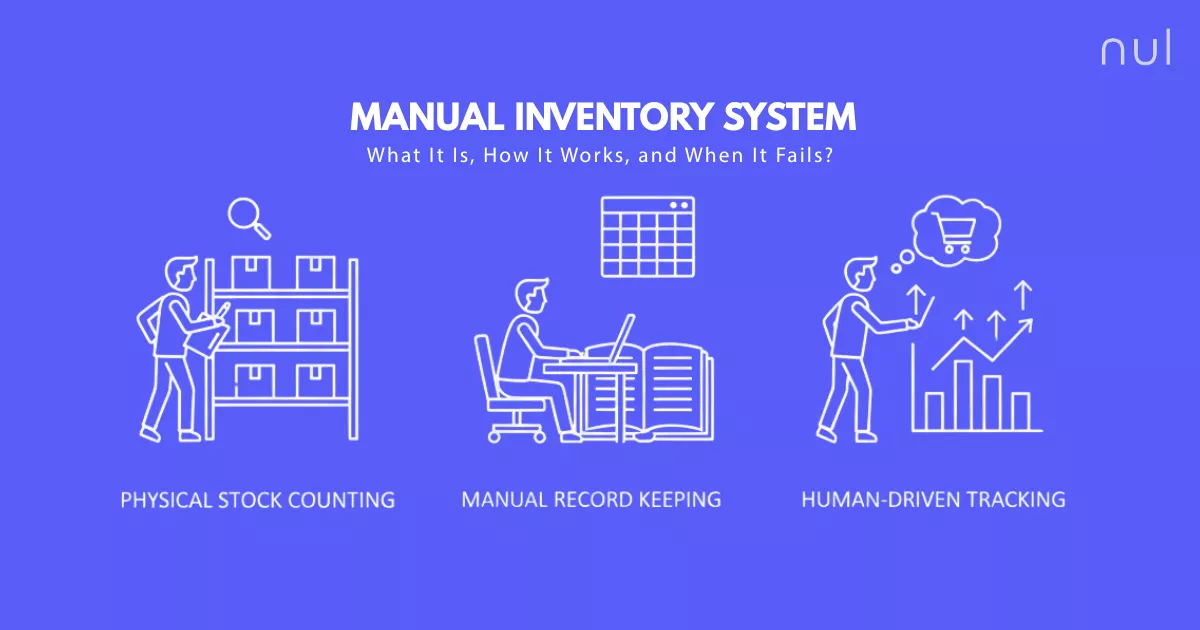
What Is Inventory Replenishment?
Inventory replenishment is the process of restocking products to ensure you maintain the right balance between supply and demand. It ensures that popular items are always available while preventing overstock of slow-moving goods.
Example: A fashion brand notices that its best-selling jeans are down to 50 units. Based on historical sales and supplier lead times, they trigger a replenishment order of 200 units to avoid stockouts during peak shopping season.
Inventory Replenishment Process
The replenishment cycle typically follows four steps:
Monitor: Track sales velocity, stock levels, and turnover rates. This gives early signals when inventory is moving faster or slower than expected.
Forecast: Predict future demand using historical data and seasonality. Even basic forecasting models can prevent common mistakes like overbuying.
Order: Place purchase orders with suppliers or transfer stock from warehouses or between locations. The timing and accuracy here directly affect service levels.
Restock: Once goods arrive, they’re received, recorded in POS systems, and made available to sell. Smooth restocking ensures sales teams and customers never feel gaps.
The role of data and automation is crucial here—manual guesswork often leads to understocking or excess stock.

Inventory Replenishment Process
Common Inventory Replenishment Methods
Periodic Replenishment: Stock is reviewed at set intervals (e.g., monthly, weekly). Best for predictable demand cycles.
Example: A clothing brand reviews sales at the end of each month and places replenishment
Just-In-Time (JIT): Goods are ordered only when needed, reducing carrying costs. Best for businesses with reliable suppliers and lean operations.
Example: A boutique relies on local suppliers to deliver accessories like belts or scarves within days, so it doesn’t need to keep large quantities in stock. This frees up capital for trend-sensitive items.
Top-Off Method: Small restocks are made frequently to “top off” shelves. Best for high-turnover, fast-moving items.
Example: An online retailer restocks fast-selling sneakers every night after order fulfillment slows, ensuring pickers always have inventory ready for the next day’s rush.
On-Demand Replenishment: Triggered when stock falls below a set reorder point. Best for eCommerce and retail POS systems.
Example: A fashion chain’s POS system flags when a new-season dress in a popular size drops below 10 units, sending a replenishment request to the warehouse to avoid gaps on the sales floor.
>> Read more: Perpetual vs Periodic Inventory System: Which to Choose?

Inventory Replenishment Methods
Factors That Influence Replenishment Decisions
Lead Time & Supplier Reliability: How quickly suppliers can deliver stock. Long or unpredictable lead times increase the need for buffer stock.
Safety Stock Levels: Buffer inventory to cover demand spikes or delays.
Seasonality & Demand Swings: Peaks like holidays or fashion seasons.
Cash Flow & Carrying Costs: Balancing stock investment with liquidity.
Benefits of Effective Inventory Replenishment
Balanced stock levels: Products are available without tying up too much capital.
Reduced costs and waste: Avoids both overstocks that sit idle and stockouts that force emergency shipments.
Improved order fulfillment and customer experience: Customers find what they want, when they want it.
Greater operational efficiency: Teams spend less time firefighting and more time planning.
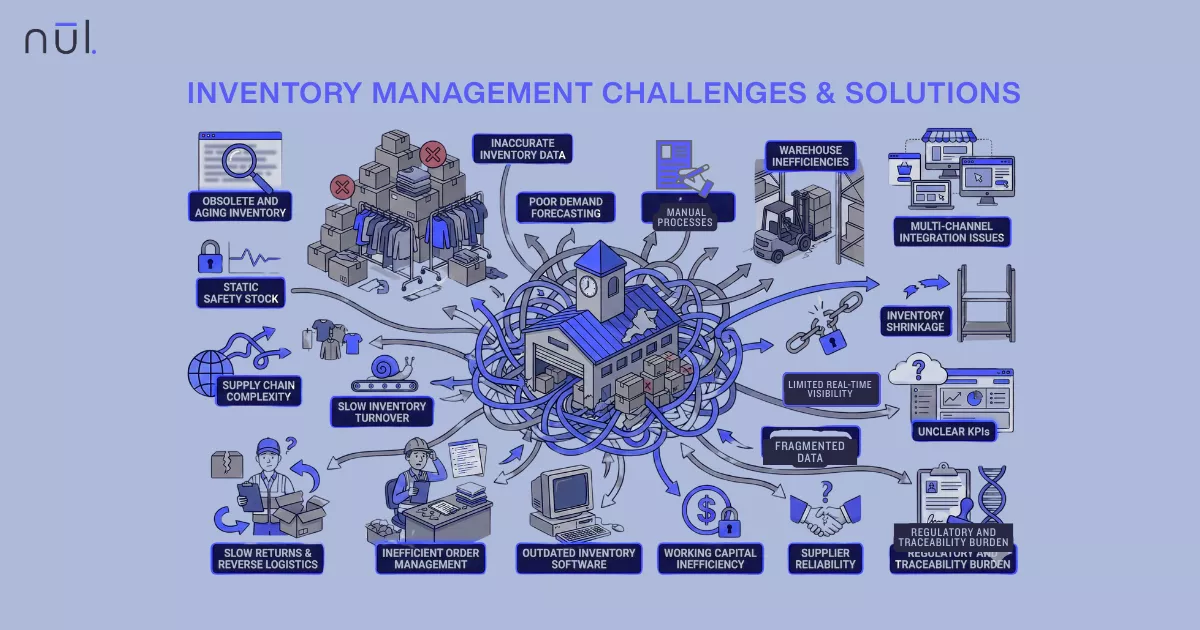
Challenges in Inventory Replenishment
Inaccurate forecasting: Wrong demand predictions lead to either shortages or surpluses.
Supply chain disruptions: Wrong demand predictions lead to either shortages or surpluses.
Overstocking/understocking risks: Both drain resources—capital, space, or customer trust.
Multi-location complexity: Coordinating stock across warehouses, stores, or channels is difficult without strong systems.
Best Practices for Optimizing Replenishment
Use real-time tracking across channels and warehouses
Set reorder points and safety stock with data, not guesswork
Monitor KPIs like service level, sell-through, and inventory turnover
Use modern inventory replenishment software solutions to reduce manual works and human erros, and speed up process with automation.
>> Read more: 7 Best AI-Powered Demand Forecasting Tools for Fashion
Optimize Inventory Replenishment with Nūl
At Nūl, we help retailers move beyond reactive stock management with AI-driven replenishment strategies.
Forecasting Integration: Predict demand more accurately at SKU, store, and channel levels
Automated Triggers: Generate replenishment orders when thresholds are reached
Omnichannel Replenishment: Align stock decisions across eCommerce, POS, and warehouses
Profit + Sustainability: Reduce waste while improving margins and sell-through
By leveraging Nūl’s agentic AI, brands can manage replenishment seamlessly, ensuring they’re never caught off guard by demand swings or supply disruptions.
Conclusion
Effective inventory replenishment ensures that businesses maintain availability without overspending on excess stock. By applying the right methods, tracking the right metrics, and using intelligent inventory tools, brands can achieve better margins, smoother operations, and happier customers.
The takeaway: don’t leave replenishment to chance. Adopt smarter strategies—and consider platforms like Nūl to bring automation, intelligence, and sustainability into your replenishment process.

Article by
Nūl Content Team
An Experienced Research & Knowledge Team
The Nūl Content Team combines expertise in technology, fashion, and supply chain management to deliver clear, practical insights. Guided by Nūl’s mission to end overproduction, we create content that helps brands forecast demand more accurately, optimize inventory, and build sustainable operations. Every piece we publish is grounded in real-world experience, ensuring it’s both credible and actionable.
LinkedIn Profile
More From Blog
Co-Build With Us
We are so keen to get this right. If the problem statement resonates, please reach out and we’d love to co-build with you so fits right into your existing workflow.

Co-Build With Us
We are so keen to get this right. If the problem statement resonates, please reach out and we’d love to co-build with you so fits right into your existing workflow.


Co-Build With Us
We are so keen to get this right. If the problem statement resonates, please reach out and we’d love to co-build with you so fits right into your existing workflow.


More From Blog


Inventory Replenishment: Process, Methods, Best Practices
Sep 30, 2025
Inventory replenishment is the process of restocking products to maintain the right balance between supply and demand, and prevent overstock of slow-moving goods.
Inventory is the lifeblood of any business—whether you’re a fashion retailer, an eCommerce brand, a wholesaler, or a manufacturer. Too little stock, and you lose sales. Too much, and you tie up cash while risking waste. That’s where inventory replenishment comes in.
This article explains what inventory replenishment is, how the process works, the methods businesses use, common challenges, and best practices for getting it right.
What Is Inventory Replenishment?
Inventory replenishment is the process of restocking products to ensure you maintain the right balance between supply and demand. It ensures that popular items are always available while preventing overstock of slow-moving goods.
Example: A fashion brand notices that its best-selling jeans are down to 50 units. Based on historical sales and supplier lead times, they trigger a replenishment order of 200 units to avoid stockouts during peak shopping season.
Inventory Replenishment Process
The replenishment cycle typically follows four steps:
Monitor: Track sales velocity, stock levels, and turnover rates. This gives early signals when inventory is moving faster or slower than expected.
Forecast: Predict future demand using historical data and seasonality. Even basic forecasting models can prevent common mistakes like overbuying.
Order: Place purchase orders with suppliers or transfer stock from warehouses or between locations. The timing and accuracy here directly affect service levels.
Restock: Once goods arrive, they’re received, recorded in POS systems, and made available to sell. Smooth restocking ensures sales teams and customers never feel gaps.
The role of data and automation is crucial here—manual guesswork often leads to understocking or excess stock.

Inventory Replenishment Process
Common Inventory Replenishment Methods
Periodic Replenishment: Stock is reviewed at set intervals (e.g., monthly, weekly). Best for predictable demand cycles.
Example: A clothing brand reviews sales at the end of each month and places replenishment
Just-In-Time (JIT): Goods are ordered only when needed, reducing carrying costs. Best for businesses with reliable suppliers and lean operations.
Example: A boutique relies on local suppliers to deliver accessories like belts or scarves within days, so it doesn’t need to keep large quantities in stock. This frees up capital for trend-sensitive items.
Top-Off Method: Small restocks are made frequently to “top off” shelves. Best for high-turnover, fast-moving items.
Example: An online retailer restocks fast-selling sneakers every night after order fulfillment slows, ensuring pickers always have inventory ready for the next day’s rush.
On-Demand Replenishment: Triggered when stock falls below a set reorder point. Best for eCommerce and retail POS systems.
Example: A fashion chain’s POS system flags when a new-season dress in a popular size drops below 10 units, sending a replenishment request to the warehouse to avoid gaps on the sales floor.
>> Read more: Perpetual vs Periodic Inventory System: Which to Choose?

Inventory Replenishment Methods
Factors That Influence Replenishment Decisions
Lead Time & Supplier Reliability: How quickly suppliers can deliver stock. Long or unpredictable lead times increase the need for buffer stock.
Safety Stock Levels: Buffer inventory to cover demand spikes or delays.
Seasonality & Demand Swings: Peaks like holidays or fashion seasons.
Cash Flow & Carrying Costs: Balancing stock investment with liquidity.
Benefits of Effective Inventory Replenishment
Balanced stock levels: Products are available without tying up too much capital.
Reduced costs and waste: Avoids both overstocks that sit idle and stockouts that force emergency shipments.
Improved order fulfillment and customer experience: Customers find what they want, when they want it.
Greater operational efficiency: Teams spend less time firefighting and more time planning.
Challenges in Inventory Replenishment
Inaccurate forecasting: Wrong demand predictions lead to either shortages or surpluses.
Supply chain disruptions: Wrong demand predictions lead to either shortages or surpluses.
Overstocking/understocking risks: Both drain resources—capital, space, or customer trust.
Multi-location complexity: Coordinating stock across warehouses, stores, or channels is difficult without strong systems.
Best Practices for Optimizing Replenishment
Use real-time tracking across channels and warehouses
Set reorder points and safety stock with data, not guesswork
Monitor KPIs like service level, sell-through, and inventory turnover
Use modern inventory replenishment software solutions to reduce manual works and human erros, and speed up process with automation.
>> Read more: 7 Best AI-Powered Demand Forecasting Tools for Fashion
Optimize Inventory Replenishment with Nūl
At Nūl, we help retailers move beyond reactive stock management with AI-driven replenishment strategies.
Forecasting Integration: Predict demand more accurately at SKU, store, and channel levels
Automated Triggers: Generate replenishment orders when thresholds are reached
Omnichannel Replenishment: Align stock decisions across eCommerce, POS, and warehouses
Profit + Sustainability: Reduce waste while improving margins and sell-through
By leveraging Nūl’s agentic AI, brands can manage replenishment seamlessly, ensuring they’re never caught off guard by demand swings or supply disruptions.
Conclusion
Effective inventory replenishment ensures that businesses maintain availability without overspending on excess stock. By applying the right methods, tracking the right metrics, and using intelligent inventory tools, brands can achieve better margins, smoother operations, and happier customers.
The takeaway: don’t leave replenishment to chance. Adopt smarter strategies—and consider platforms like Nūl to bring automation, intelligence, and sustainability into your replenishment process.


Article by
Nūl Content Team
An Experienced Research & Knowledge Team
An Experienced Research & Knowledge Team
The Nūl Content Team combines expertise in technology, fashion, and supply chain management to deliver clear, practical insights. Guided by Nūl’s mission to end overproduction, we create content that helps brands forecast demand more accurately, optimize inventory, and build sustainable operations. Every piece we publish is grounded in real-world experience, ensuring it’s both credible and actionable.
LinkedIn Profile